Introduction
Lower back pain has become a global epidemic in recent years.
Back pain affects about 619 million individuals around the world, making it one of the most common causes of disability. According to the WHO, this number is expected to increase to 843 million by 2050.
Observed in October, World Spine Day creates a platform that discusses and educates the masses on the importance of protecting spine health, measures to reduce the risk of spinal problems, and the significance of timely interventions.
People can live active, pain-free lives if they know about spinal disorders, how to spot them early, and what treatments are available.
What is World Spine Day?

World Spine Day, which is sometimes referred to as “Spine Health Day,” is a global event hosted by the World Federation of Chiropractic (WFC) that takes place every year on October 16.
The goal of this observance is to urge people to be active, keep their backs straight, and get care for spinal problems as soon as they happen. It brings together health care workers, wellness experts, and communities to spread the word on the importance of maintaining spine health and reducing the risk of spinal problems.
History of World Spine Day
The first World Spine Day was observed in 2008, and the first formal celebration was in 2012.
It has since turned into one of the biggest movements in the world to raise awareness about education, prevention, and rehabilitation in order to lessen the global burden of spinal illnesses.
2025 World Spine Day Theme
The theme for World Spine Day 2025 is "Invest in Your Spine."
It focuses on helping people have access to the education and tools they need to improve their spine health by adopting spine-healthy habits, staying physically active, using ergonomics, and opting for multidisciplinary spine care.
The campaign urges people and healthcare organisations to put time, knowledge, and money toward preventing and treating back pain effectively.
Global Impact of Spinal Disorders
Spinal disorders are among the most common reasons for long-term disability and chronic pain. Low back pain is the most common cause of years lived with disability (YLDs) in the world.
Millions of people in both developed and developing countries are affected by degenerative diseases, spinal injuries, or work-related stress, which have severely impacted their quality of life and overall well-being.
By making spinal health a public priority, healthcare systems can lower disability rates and improve quality of life.
Common Spinal Problems
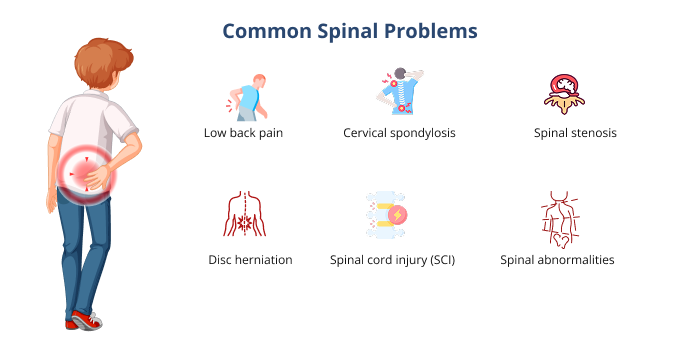
While low back pain is one of the most common spinal problems, there are other spinal problems, too.
- Low back pain: This is often caused by bad posture, lifting heavy things, or degenerative disc disease.
- Cervical spondylosis: It refers to the damage to the neck area that happens with age.
- Spinal stenosis: It occurs when the spinal canal gets narrower, which puts pressure on the nerves.
- Disc herniation: This condition occurs when a disc has slipped or broken and is pressing on nerves nearby.
- Spinal cord injury (SCI): This usually happens because of an accident, trauma, or fall.
- Spinal abnormalities: Spinal abnormalities, such as scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis, can occur due to congenital factors or age-induced degeneration.
Comprehensive Guide to Spine Surgery Types
With advancements in technology and precision, the landscape of spinal care has transformed drastically. Today, specialists are able to recommend treatment options based on the individual needs of the patient and support them in returning to the best state of health possible.
The following are the different spinal care treatment approaches:
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Most spine disorders can be treated with non-surgical approaches, which primarily involve adopting spine-friendly lifestyle habits. Some common non-surgical methods are:
- Physical treatment and exercise programs that are specific to your needs
- Pain and inflammation medications
- Posture corrections and ergonomic adjustments
- Healthy weight management
- Procedures for managing pain, such as epidural injections
Conservative Management
Rehabilitation and prevention are the main goals of conservative management.
Conservative management of spine health comprises manual therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, and physiotherapy.
These approaches aim at improving movement, building up core muscles, and reducing the need for painkillers.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS)
With MISS, the cuts or incisions are smaller, the tissue damage is minimal, and the recuperation time is shorter.
It works especially well for diseases like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or operations to relieve pressure. Patients lose less blood, remain in the hospital for less time, and feel less pain after surgery.
Advanced Surgical Procedures
Advanced surgical procedures are recommended when non-surgical approaches fail to manage the condition.
The following are the different advanced or complex spine surgery approaches recommended, depending on the condition.
Spinal fusion: Spinal fusion alleviates pain by stabilising two or more vertebrae.
Disc replacement: During disc replacement, the surgeon inserts new, artificial discs to replace damaged ones.
Fixing deformities: Deformity corrections are performed to correct scoliosis and other spinal deformities and restore the function and mobility.
Complex revision surgeries: For people who have had spinal problems before or who have had surgery with poor outcomes, revision surgeries are recommended.
Essential Spine Care Tips
Taking good care of your spine is imperative for your overall well-being. Prioritise your spine health with the following spine care tips:
- Keep your posture straight while you sit, stand, or lift.
- Exercise regularly; walking, swimming, and stretching are all great options.
- Use beds and furniture that support proper spinal alignment.
- Don't sit for long periods of time at your desk, and take breaks often.
- Stop smoking and keep your weight in check, as both might make your spine worse.
- To avoid abrupt strain, practice the right way to lift things.
Preventive Strategies
When it comes to taking care of your spine, it goes without saying that prevention is better than cure. With the right lifestyle habits, you can strengthen your spine and keep various spinal problems at bay.
- Avoid sitting or not moving for too long. Consider going on a short walk or doing some movement exercises at regular intervals.
- The way you lift heavy objects can also have an impact on your spine health. Using your back (bending your back) while lifting objects can damage the spine. Instead, you should bend your legs. Learning proper lifting techniques can help you protect your spine.
- Paying attention to back pain and mobility-related issues in early stages is important for timely interventions and a better quality of life.
Diagnosis and Treatment
For good spine care, it's very important to have the right diagnosis. Diagnostic techniques encompass:
Physical Exam and Medical History Assessment: When you see a doctor for back pain, they will initially conduct a physical examination to determine the underlying cause of your back pain. They will also discuss your medical history and family history.
If the initial evaluation points towards spinal problems, additional tests will be recommended for a detailed evaluation.
Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs are commonly recommended imaging tests to diagnose spinal conditions.
Neurological Tests: Patients are made to undergo neurological tests to assess their motor skills, sensory skills, reflexes, coordination, and balance. Nerve conduction tests may also be recommended.
Lumbar Puncture: In some cases, doctors will recommend a lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, which involves collecting the cerebrospinal fluid from the spine and examining it for signs of infection or other problems.
Bone Scan: Bone scans are recommended to look for malignancies and degenerative diseases.
Treatment Planning
Based on the diagnostic information from the tests conducted, doctors will devise a personalised treatment strategy, which can include one or more treatments, depending on the severity of the condition.
Different treatment options available include lifestyle modifications, physiotherapy, medications, and surgery.
Treatment Delivery and Recovery
Once the patient agrees to undergo treatment as per the plan recommended, the treatment will begin. After the treatment is completed, they may be expected to see the doctor for regular follow-up appointments.
During recovery, if the patient experiences any complications or side effects, they should connect with the doctor for necessary care and support.
When to Seek Professional Help
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention
Early intervention or treatment plays a critical role in the effective management of spinal problems. Paying attention to spinal symptoms and undergoing necessary evaluation is crucial to preserving your spine health.
Do not ignore the following spine-related symptoms:
- Back or neck ache that doesn't go away after a few weeks
- Pain that goes down the arms or legs
- Weakness, tingling, or numbness in the arms and legs
- Pain makes it hard to walk, balance, or sleep
- Not being able to control your urine or bowels
If you experience the following symptoms, please see a doctor for a detailed evaluation.
Treatment Decision Timeline
0 to 6 weeks: In the early stages, doctors try to manage spine issues through physiotherapy and conservative care.
6 to 12 weeks: If there are no improvements, doctors will recommend diagnostic tests to find out the underlying cause. Pain management strategies may be recommended during this phase.
12 weeks and after: If the pain or discomfort does not go away even after 12 weeks, the doctor may recommend surgical interventions. The type of surgery recommended may depend on the severity of the spinal problem.
Post-treatment recovery: The recovery period may vary anywhere between 6 and 12 months. During this period, patients must adhere to the follow-up guidelines shared by the expert team.
Importance of Supportive Care Available at Multispeciality Hospitals
Multispeciality hospitals offer a comprehensive approach to spine care by bringing together orthopedic spine surgeons, neurosurgeons, physiotherapists, and rehabilitation specialists.
This collaboration makes sure that accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and long-term rehabilitation all happen in one place.
Finding the Best Spine Hospital in Ahmedabad
HCG Hospitals is considered one of the best spine hospitals in Ahmedabad. It is equipped with highly advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities, with which our doctors treat all major spine-related conditions.
With a special focus on the patient’s quality of life, our specialists devise customized and patient-focused treatment strategies that address the specific health needs of each patient.
Looking for the best spine surgeon in Ahmedabad? Connect with HCG Hospitals today.
World Spine Day: Global and Local Observances
World Spine Day is observed worldwide through posture-awareness initiatives, ergonomic workshops, community fitness events, and hospital-led spine-screening camps.
In India, many hospitals and rehabilitation centers run initiatives to raise awareness about spine health and teach staff, students, and families.
Conclusion
The message on World Spine Day 2025 is clear: Invest in Your Spine. Become aware of the habits that affect your spine health, learn about the early symptoms of spine problems, and know when to seek medical intervention for your condition.
With regular exercise, appropriate posture, and timely treatment, spinal diseases can be prevented or effectively treated. Putting spinal health first benefits you with increased mobility, independence, and a better quality of life, whether it's through lifestyle changes or more complex surgeries.