Introduction
You may have come across hundreds of posts and videos on YouTube and other social media platforms explaining how iron deficiency can hamper normal body function and cause various complications.
Iron deficiency is a common condition among the Indian population, especially women. Menstruation, pregnancy, and certain lifestyle habits are key reasons for iron deficiency in women. In the early stages, this condition may not cause any symptoms. However, as the deficiency becomes severe, women may begin to experience various symptoms.
Hence, seeking care and promptly addressing this deficiency is crucial for maintaining optimum health.
In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know—from the early symptoms of iron deficiency to the best ways to treat and prevent it.
What is Iron Deficiency?
Iron is a vital mineral that allows oxygen to be transported into the blood. It is also a key component of haemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that binds oxygen and transports it to the rest of the body from the lungs. Too little iron prevents the body from producing sufficient healthy red blood cells, leading to iron deficiency.
Causes of iron deficiency may include inadequate intake, poor absorption, or chronic blood loss. The body stores iron within muscles, bone marrow, and organs like the liver; however, these reserve supplies may also start to dwindle if demand for iron remains high with little in return.
If not treated, low levels of iron in women can worsen and lead to iron deficiency anaemia. This condition significantly impairs oxygen delivery to tissues, resulting in fatigue, shortness of breath, heart issues, cognitive issues, an increased susceptibility to infections, and pregnancy complications.
Early Signs of Iron Deficiency Women Shouldn’t Ignore
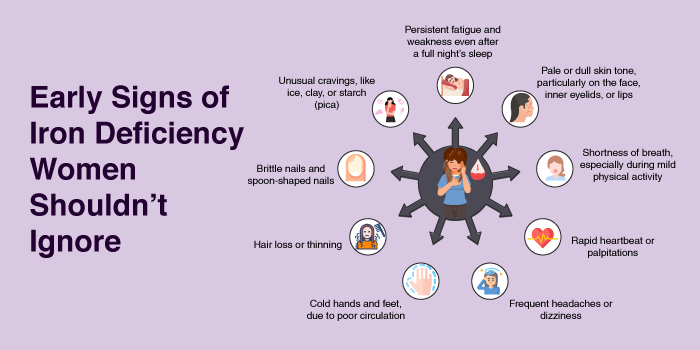
Many women dismiss the symptoms of iron deficiency as common fatigue or stress, but ignoring these warning signs can be dangerous. Here are the early signs of iron deficiency that women should pay close attention to:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness even after a full night’s sleep
- Pale or dull skin tone, particularly on the face, inner eyelids, or lips
- Shortness of breath, especially during mild physical activity
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Frequent headaches or dizziness
- Cold hands and feet, due to poor circulation
- Hair loss or thinning
- Brittle nails and spoon-shaped nails
- Unusual cravings, like ice, clay, or starch (pica)
Some women may also have mood changes, a foggy brain, and irritability. One must know how to identify various signs of iron deficiency and seek timely treatment to reduce the risk of serious complications.
Causes of Iron Deficiency in Women
Knowing why someone lacks iron is important for creating a unique way of helping them treat the problem. The following are the common causes of iron deficiency in women:
1. Menstruation
Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding is one of the leading causes of low iron levels in women. Each menstrual cycle can deplete iron, especially if not replenished through diet or supplements.
2. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
During pregnancy, the body’s iron requirement increases to support foetal growth, placental development, and increased blood volume. Iron is also passed to the baby through breast milk, further depleting maternal stores.
3. Dietary Deficiency
Women who follow a vegetarian, vegan, or restrictive diet may not get sufficient iron, as iron from plant-based sources (non-heme iron) is harder for the body to absorb.
4. Gastrointestinal Conditions
Issues like coeliac disease, Crohn’s disease, or gastric bypass surgery can impair the body’s ability to absorb iron efficiently.
5. Chronic Blood Loss
Conditions such as ulcers, polyps, or even frequent blood donation can lead to chronic blood (and iron) loss over time.
Understanding these causes helps in determining the right treatment strategy. Women who experience any combination of these symptoms should consider regular checkups at HCG, the best multispecialty hospital in India for preventive care.
Who’s Most at Risk for Iron Deficiency?
Certain populations are at higher risk for iron deficiency. These include:
- Teenage girls with irregular or heavy periods
- Pregnant or postpartum women
- Women with a history of anaemia or nutritional deficiencies
- Vegetarians or vegans
- Endurance athletes, especially runners, due to gastrointestinal blood loss and increased iron turnover
- Women with chronic diseases, such as kidney disease or gastrointestinal disorders
If you fall into any of these groups, regular screening for iron deficiency is essential to reduce the risk of various complications.
How to Diagnose Iron Deficiency Quickly
Early diagnosis is crucial for the effective management of iron deficiency. Fortunately, the diagnosis of iron deficiency in women is done through simple blood tests:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): Measures red blood cell count and haemoglobin.
- Serum Ferritin: Reflects the amount of stored iron in the body. Low levels indicate iron deficiency.
- Serum Iron and Total Iron-Binding Capacity (TIBC): Evaluate how much iron is in your blood and how well it binds to transport proteins.
- Transferrin Saturation: Measures the percentage of transferrin (a protein) bound to iron.
Many hospitals and clinics offer same-day results, enabling quicker interventions.
For accurate testing and expert care, you may visit a nearby hospital, which has experienced haematologists or general physicians who can help you receive proper care.
Fast & Effective Ways to Fix Iron Deficiency
Thankfully, there are many ways to correct low iron levels in women and regain optimal health. Your treatment may include:
1. Iron-Rich Diet
Consume foods high in heme iron (easier to absorb), such as:
- Red meat (beef, lamb)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey)
- Liver and organ meats
- Shellfish (clams, oysters)
For plant-based options:
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Fortified cereals and grains
- Pumpkin seeds, tofu, and quinoa
Pair iron-rich meals with vitamin C (like citrus fruits or tomatoes) to enhance absorption of this mineral.
2. Iron Supplements
Iron pills or capsules are commonly recommended for a fast increase in iron levels.
Iron supplements should be taken with medical advice, as too much iron can lead to vomiting, constipation, and organ damage.
3. Intravenous (IV) Iron Therapy
IV iron infusions may be recommended in cases of moderate to severe iron deficiency.
IV iron therapy is administered under medical supervision, usually at advanced facilities.
At HCG Hospitals, one of the best multispeciality hospitals in India, we offer various treatment approaches, including IV iron therapy, for iron deficiency management.
4. Address Underlying Conditions
If your iron loss is due to menstrual cycles, gastrointestinal bleeding, or a chronic condition, managing the root cause is essential for long-term improvement.
Conclusion
Iron deficiency in women is a common but often underdiagnosed condition that can significantly affect energy, immunity, and daily functioning. Recognising the symptoms of iron deficiency early on allows for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
It is possible to replenish the iron levels through diet change, supplementation, and infusion therapy.
Contact the top multispecialty hospitals in India, like HCG Hospitals, for a precise diagnosis, individualised care, and continuing support.