
Home / Blog / Diarrhea and Fever in Children: Signs, Causes, and Remedies
Children frequently experience diarrhoea and fever, which can be distressing for both the child and parents. While these symptoms are often caused by minor infections, they can sometimes indicate more serious conditions. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and appropriate treatments is essential for managing diarrhoea in children effectively.
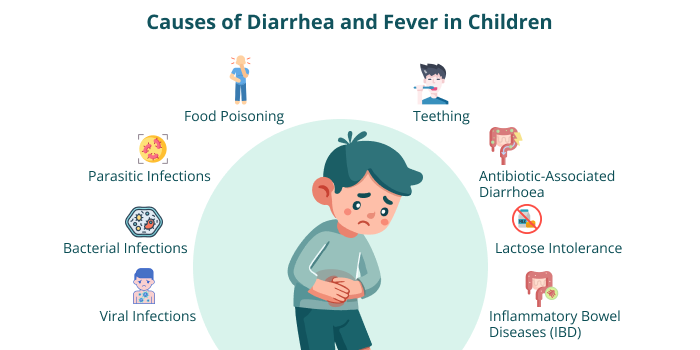
Viruses like rotavirus and norovirus are among the most common fever and diarrhoea causes among children. These infections typically spread through contaminated food, water, or close contact with an infected person. Symptoms often include watery diarrhoea, fever, vomiting, and dehydration, lasting between three and seven days.
Bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Shigella can lead to paediatric diarrhoea treatment challenges. These infections often result from consuming contaminated food or drinks and may require medical intervention. Symptoms include severe diarrhoea, fever, stomach pain, and sometimes blood in the stool.
Children may have diarrhoea for a long time due to parasites such as Giardia. The infection is usually transmitted as a result of dirty water and a lack of cleanliness. They often lead to persistent watery stools, bloating, fatigue, and mild fever.
Contaminated food can introduce harmful toxins that trigger sudden episodes of diarrhoea and fever. Symptoms typically develop quickly and may include vomiting, nausea, stomach pain, and sometimes fever. Proper food handling and storage are crucial in preventing foodborne illnesses.
A few babies get a slight paediatric fever and loose stools when teething. Nevertheless, teething alone does not cause diarrhoea. The excess saliva in the mouth and the habit of inserting things into the mouth could expose one to germs that cause disorders in the digestive system.
Some antibiotics can upset the normal germs in the belly and cause loose stool in kids. The illness goes away after taking the medication. Probiotics or yoghurt with live bacteria could restore the normal intestinal bacteria and make the symptoms better.
Some children are unable to digest lactose properly, leading to bloating, gas, and diarrhoea after consuming dairy products. Symptoms may occur within a few hours of ingesting milk, cheese, or ice cream and can be managed by avoiding dairy or using lactose-free alternatives.
Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause chronic diarrhoea in children, sometimes accompanied by paediatric fever and abdominal pain. These autoimmune conditions require medical management and dietary modifications.
Seek medical attention if your child experiences:
Additional Reading: When to See a Gastroenterologist for Stomach Pain: Key Signs and Symptoms | HCG Hospitals

Although it is usual for children to experience diarrhoea and fever, it is important to know what brings about these diseases as well as their signs so that they can be treated properly. Many instances end up well after receiving the right attention, but there are times when a doctor’s intervention becomes imperative. To get expert advice, consult a paediatric specialist at a leading multispeciality hospital in India, like HCG Hospitals.