Home / Blog / Brain Hemorrhage: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Recovery Insights
A brain haemorrhage, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a type of stroke that happens when there is bleeding in the brain or around it. It occurs due to the bursting of blood vessels within the brain, which causes high pressure on adjacent tissues. This condition can be life-threatening and therefore needs a doctor’s help immediately. The severity and location of the brain bleed determine the impact on a person’s brain function.
Brain haemorrhages can be classified into different types based on their location:
Also Read: A Comprehensive Guide to Neurosurgery | HCG Hospitals
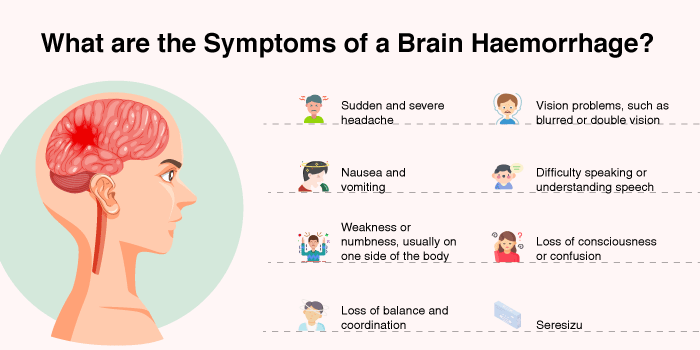
The symptoms of a brain haemorrhage vary based on the severity and location of the bleeding. Common symptoms include:
Click Here: To learn more about Neurological Disorders
Several factors can lead to a brain haemorrhage, including:
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of a brain haemorrhage, seek medical help immediately. Some urgent signs requiring emergency interventions include:
It is very important to get medical help immediately if someone has a brain haemorrhage. To diagnose intracranial haemorrhage, healthcare professionals use CT scans or MRIs.
Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the brain haemorrhage:
After initial brain haemorrhage treatment, rehabilitation is often necessary to regain lost functions. This may include:
The recovery time for a brain haemorrhage depends on its severity and the treatment response shown by the patient. The recovery timeline for a brain haemorrhage can comprise:
Recovery can be a challenging phase for brain haemorrhage patients because one may not be able to move well, think properly, speak clearly, or control their emotions. However, with therapy and family support, patients can overcome these complications and lead a better life.
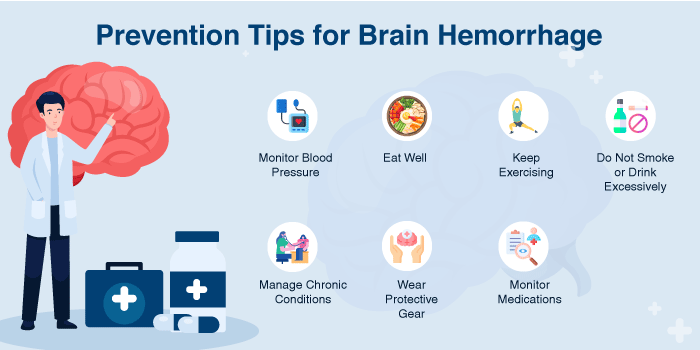
Preventing brain haemorrhages involves managing risk factors and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
A brain haemorrhage is a critical illness that needs urgent medical care. Recognising the signs, reasons, and available brain haemorrhage treatment may facilitate timely identification and action. Although it may be difficult to get better, rehab and lifestyle modifications make sure that the person has a healthy life. The risk of intracranial haemorrhage can be greatly lowered by controlling risk factors and taking precautions.
Also Read: Brain Aneurysm, its Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
A brain haemorrhage is manageable, but full recovery depends on the severity. First aid, operation, and therapy aid in controlling signs of illness and restoring normal body activities, although with certain irreversible consequences.
Long-term effects may include weakness, speech problems, memory loss, vision impairment, emotional changes, or difficulty with coordination. Rehabilitation can help improve the quality of life for patients and regain lost abilities over time.
To keep your blood pressure normal, exercise, eat well, don’t smoke or drink too much, control long-term illnesses, use protective clothing, and speak with your doctor to know if you need a prescription for anticoagulants.
Survival rates vary based on severity, age, and treatment. Around 40–50% of severe cases are fatal, but timely medical care and rehabilitation significantly improve survival and recovery chances.
Yes, rehabilitation is crucial for regaining lost functions. Physical, speech, and occupational therapy help improve mobility, communication, and daily activities, enhancing recovery and long-term independence.