Home / Blog / Kidney Stones: Causes, Treatment Methods, and Prevention Tips
A kidney stone is a hard deposit of minerals & acid salts that forms in the kidney.
When high levels of calcium, oxalate, and uric acid in the urine crystallise, it leads to the development of uric acid stones.
Although tiny kidney stones can pass through the urinary tract with little or no pain, bigger ones may cause intense pain and discomfort.
Kidney stones are common and affect millions of people worldwide. They can vary in size, shape, and composition, with some being as small as a grain of sand and others growing to the size of a golf ball. If not treated, kidney stones can cause infections and harm the kidneys; therefore, timely kidney stone diagnosis and kidney stone treatment are crucial.
Anyone can get kidney stones, although some people are at higher risk. Their formation is influenced by various factors, including lifestyle, genetics, and underlying medical conditions, which play a significant role in their formation.
Understanding these factors can help in both early kidney stone diagnosis and preventive care, reducing the likelihood of recurrent kidney stones in susceptible individuals.
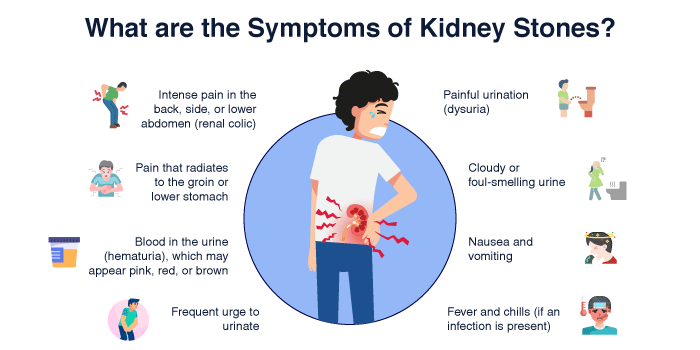
The size and position of kidney stones determine the signs. There are times when certain stones block the ureter and do not show any symptoms in the kidney, but this leads to intense pain as well as discomfort. Some common signs are:
Pain from kidney stones can come in waves and fluctuate in intensity, often making it difficult for individuals to find a comfortable position. The presence of stones may obstruct urine passage, thus predisposing the individual to other problems like UTI or hydronephrosis.
If you experience severe pain or other concerning symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications.
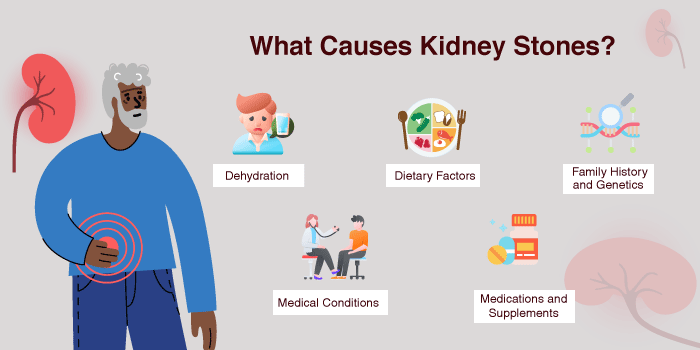
Several factors contribute to the formation of kidney stones. The primary causes of kidney stones include:
Lack of adequate water intake can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of crystal formation and kidney stone development.
Certain foods can contribute to kidney stone formation, such as those high in oxalates (e.g., spinach, beets, nuts), excessive salt, and high-protein diets, especially non-vegetarian food substances.
A family history of kidney stones increases the likelihood of developing them.
Certain health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, and urinary tract infections, can increase the risk of kidney stones.
Certain drugs, like diuretics and excessive amounts of vitamin D and calcium, as well as antacids with calcium, can contribute to kidney stone formation.
Kidney stones can form when the body fails to process minerals properly due to hormonal imbalances and metabolic disorders. Moreover, people who have undergone gastric bypass surgery or have long-term digestive disorders may also have altered nutrient absorption, which makes them more likely to develop kidney stones.
If kidney stones are suspected, your doctor will need a confirmed kidney stone diagnosis with detailed information, such as the size and location of the stone.
Commonly recommended tests for kidney stone diagnosis include:
Your doctor will review your medical history, symptoms, and any underlying conditions that may contribute to kidney stones.
A urine test can detect blood, minerals, and infections, providing insight into the composition of kidney stones.
Blood tests can help identify high levels of calcium, uric acid, or other substances that may contribute to kidney stone formation.
Kidney stone treatment depends on the kidney stone type, size, and severity of symptoms. Common options available for kidney stone treatment include:
If the kidney stone is too large or causes significant pain, medical intervention may be necessary.
Preventing kidney stones involves making lifestyle and dietary changes to reduce the risk of stones. Here are some key prevention strategies:
Drinking at least 2-3 litres of water daily helps dilute urine and prevent mineral buildup.
Obesity and metabolic disorders increase the risk of kidney stones. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help prevent stone formation.
Consult your doctor before taking high doses of calcium, vitamin D, or other supplements that could contribute to kidney stone formation.
If you have a history of kidney stones, routine checkups with a urologist can help manage risk factors.
Kidney stones are a painful yet manageable condition with proper kidney stone treatment and preventive measures. Understanding kidney stone causes, symptoms, and available treatment options can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain kidney health.