What is a Hernia?
A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak point in a muscle or connective tissue. Although they may occur anywhere, hernias are usually seen in the belly and lower abdomen.
Hernias, especially when they are small, do not cause any pain in most cases. However, as they grow, they start causing pain, and hence, prompt detection and timely treatment become necessary.
Hernias can happen to anyone, young or old. They may be either congenital or acquired as a result of stress and muscle laxity.
Also, not all hernias need immediate attention. However, if left untreated, some hernias may cause problems like blockage or strangulation, which is the turning off of the blood supply from the herniated organ, leading to tissue death.
Sometimes, hernias that are not treated may cause long-lasting pain and lack of movement, impacting daily activities and overall well-being.
Also Read: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Types of Hernia
There are several types of hernias, each affecting different areas of the body:
- Inguinal hernia: This type of hernia affects men more than women. It occurs when the intestinal parts protrude into the groin through the weaker abdominal wall. It constitutes about 70% of all hernias.
- Femoral hernia: It forms at the top of the thigh, close to the groin, and affects females more. Although not as frequent as inguinal hernias, they can lead to serious complications if left untreated.
- Umbilical Hernia: A bulge develops close to the navel when a part of the gut pushes out through the belly wall. This condition is common among children at birth but may also affect grown-ups, particularly those who are overweight or have had multiple pregnancies.
- Hiatal hernia: It occurs when a section of the stomach moves up through the diaphragm into the chest. This condition usually causes symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux and problems with swallowing.
- Incisional hernia: It occurs at the site of a previous surgical incision where the abdominal wall remains weak. These hernias can enlarge over time, requiring hernia surgery.
- Epigastric hernia: It forms between the belly button and the lower part of the ribcage, and it is caused by a gap in the abdominal muscles. It often appears as a small lump that can cause discomfort.
- Spigelian hernia: It develops along the side of the abdominal muscles and is relatively rare. Due to their location, these hernias can be harder to diagnose.
Signs and Symptoms of Hernia
Common hernia symptoms include:
- A noticeable bulge in the affected area that increases in size when standing or straining
- Pain or discomfort, especially when lifting objects, coughing, or bending over
- A burning or aching sensation at the hernia site
- Symptoms of acid reflux, heartburn, or difficulty swallowing (in the case of a hiatal hernia)
- Weakness, pressure, or heaviness in the abdomen or groin
- Nausea, vomiting, or bowel obstruction in severe cases
- Changes in bowel movements, such as constipation or bloating, particularly in cases of larger hernias
In most cases, patients do not experience any hernia symptoms early on. However, if the hernia grows or becomes strangulated, emergency medical attention may become necessary.
What Causes a Hernia?
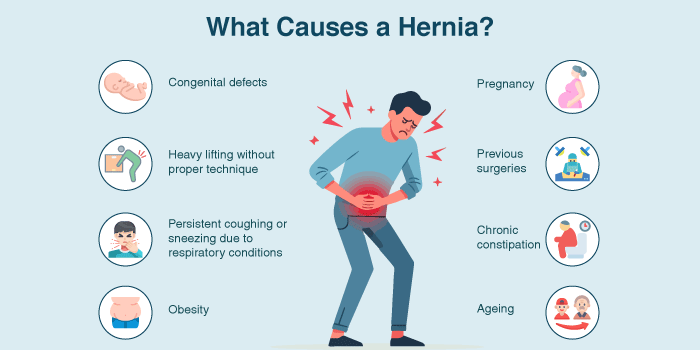
Hernias are caused by a combination of muscle weakness and strain. The following factors can contribute to hernia development:
- Congenital defects present at birth, leading to weaker muscles
- Heavy lifting without proper technique increases intra-abdominal pressure
- Persistent coughing or sneezing due to respiratory conditions like chronic bronchitis or smoking
- Obesity puts excessive pressure on the abdominal muscles
- Pregnancy, due to increased abdominal pressure and stretching of muscles
- Previous surgeries have weakened the abdominal wall
- Chronic constipation leads to excessive straining during bowel movements
- Ageing, as muscle tissues lose strength and elasticity over time
Also Read: Placental Abruption: Symptoms, Causes, and Signs of Abruptio Placentae Explained
Diagnosing a Hernia: Tests and Examinations
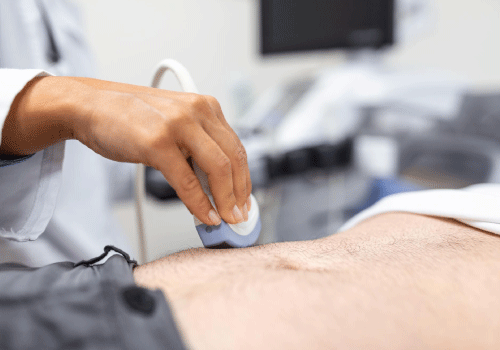
Doctors diagnose hernias through a combination of physical exams and imaging tests:
- Physical Examination: The doctor may feel the bulge and ask the patient to cough or strain to observe changes. This is usually sufficient for diagnosing external hernias.
- Ultrasound: This test helps visualise soft tissue and detect hernias, especially in children and pregnant women.
- CT scan: It provides detailed images to identify internal hernias and complications, particularly in cases where physical exams are inconclusive.
- MRI Scan: It is used in specific cases where more detailed imaging is necessary, particularly for deep or complex hernias.
- Endoscopy: It involves inserting a small camera through the throat to examine the oesophagus and stomach in cases of hiatal hernia. This test helps detect acid reflux and associated complications.
Hernia Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type, size, and severity of hernia symptoms. The following are the different treatment options for a hernia:
- Watchful Waiting: Small, asymptomatic hernias may not require immediate intervention but should be monitored regularly to detect any changes.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, weight management, and avoiding heavy lifting can help manage hernia symptoms and prevent the worsening of a hernia.
- Medications: Acid-reducing medications may be prescribed for hiatal hernias to alleviate symptoms of acid reflux. However, they do not cure the hernia itself.
- Hernia Surgery: The most effective hernia treatment involves surgical repair, which can be done using:
- Open Surgery: A traditional procedure involving a larger incision to repair the hernia with stitches or mesh. It is often used for large or complicated hernias.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: A minimally invasive approach using small incisions and a camera-guided technique for faster recovery, reduced pain, and minimal scarring.
- Robotic Surgery: A more advanced form of hernia surgery offering enhanced precision and control, reducing the risk of complications.
Many people opt for hernia surgery with mesh because, besides cutting down the chances for the sickness to return, it also gives extra strength.
The patient will get back to his normal routine in about two to three weeks after undergoing some specific care following surgery.
Conclusion
Hernias are common conditions that can range from mild to severe. Understanding the different types, causes, symptoms, and hernia treatment options is essential for early detection and management.
If you suspect a hernia, consult a specialist for a detailed evaluation. HCG Hospitals, a leading multispeciality hospital in India, has dedicated specialists for effective hernia management.
Hernia surgery remains the most effective solution for symptomatic hernias, ensuring long-term relief and preventing complications.
Hernias may not always be fatal, but they can affect how someone lives. If you see a doctor as soon as possible, it will be easier to control any symptoms of hernia, and this may also stop any dangerous problems like strangulation or bowel blockages from occurring.
Due to advanced hernia surgery techniques and better medical care, hernia treatment is now safer and works better, enabling patients to recover quickly and have improved outcomes. To reduce the risk of hernia formation, it is important to take preventive measures like managing one’s weight, avoiding too much pressure, and strengthening the core muscles.